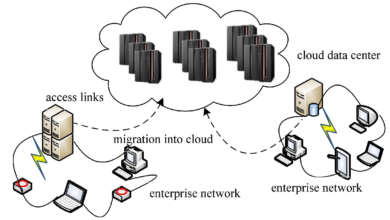
Streamlining Operations with Data Servers
In today’s fast-paced and data-driven world, businesses of all sizes are constantly looking for ways to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. One essential tool that has revolutionized the way organizations handle their data is the data server. By centralizing and organizing data, these servers play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and ensuring smooth operations. In this blog article, we will delve into the world of data servers, exploring their benefits, features, and how they can help businesses streamline their operations.
From small startups to multinational corporations, every business generates and relies on vast amounts of data. Without proper management and organization, handling this data can become a daunting task, leading to inefficiencies and potential errors. This is where data servers come into play. By storing, processing, and distributing data, these servers help businesses streamline their operations and optimize their workflows.
Understanding Data Servers: An Overview
Modern businesses require effective data management systems to handle their growing data needs. Data servers provide the infrastructure to store, process, and manage data efficiently. These servers are specialized computers designed to handle heavy data workloads, ensuring fast and reliable access to information. Data servers come in various forms, including tower servers, rack servers, and blade servers, each offering different capabilities and scalability options.
The Role of Data Servers in Business Operations
Data servers play a vital role in business operations by serving as the central hub for data storage and processing. They act as repositories for all types of data, including customer information, sales data, inventory records, and more. By centralizing data, businesses can access and manage information seamlessly, eliminating the need for multiple data sources and reducing the risk of data inconsistencies. Data servers also ensure data integrity by implementing robust security measures, backups, and disaster recovery strategies.
The Different Types of Data Servers
When choosing a data server, it is crucial to consider the specific needs and requirements of your business. Tower servers are compact and suitable for small to medium-sized businesses with limited space. Rack servers are designed to fit into standard server racks, making them ideal for businesses that require scalability and flexibility. Blade servers offer high-density computing power and are often used in data centers with extensive processing requirements. Understanding the different types of data servers will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your organization’s goals.
Centralizing Data for Improved Accessibility
In today’s digital landscape, access to data is crucial for efficient business operations. Centralizing data with a dedicated data server offers numerous benefits in terms of accessibility and ease of use. With a centralized data server, employees can access information from a single source, eliminating the need to search through multiple files or databases. This improves collaboration and allows for real-time updates, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information. Centralized data also simplifies data management, reducing the time and effort required to maintain multiple data sources.
Improved Collaboration and Real-Time Updates
A centralized data server promotes collaboration within an organization by providing a single source of truth for all employees. With real-time updates, everyone can access the most up-to-date information, reducing the risk of working with outdated or conflicting data. This fosters better decision-making and enables teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical location. Additionally, a centralized data server ensures that changes made by one employee are immediately reflected for others, eliminating the need for manual synchronization or data transfer.
Simplifying Data Management
Managing multiple data sources can be time-consuming and prone to errors. By centralizing data with a dedicated server, businesses can simplify data management processes. Updates, backups, and security measures can be implemented more efficiently, ensuring that data is consistently and accurately maintained. Centralized data also allows for easier data analysis and reporting, as information from various departments or branches can be easily consolidated. This streamlines data-driven decision-making and enables organizations to quickly identify trends, opportunities, and potential issues.
Enhancing Data Security and Protection
Data security is a top concern for businesses in today’s digital landscape. Data servers offer robust security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. By implementing encryption, firewalls, and regular backups, data servers provide a secure environment for storing and managing data.
Implementing Encryption for Data Protection
Encryption is a fundamental security measure for data servers. It involves encoding data using cryptographic algorithms, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals. With encryption in place, even if someone gains access to the data, they will not be able to decipher its contents without the encryption key. This ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and secure, mitigating the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
To protect data servers from external threats, firewalls and intrusion detection systems are essential. Firewalls act as a barrier between the server and the internet, monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic. They control access based on predefined rules, preventing unauthorized access attempts. Intrusion detection systems, on the other hand, monitor network traffic for suspicious activities or patterns that may indicate a potential security breach. By implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems, businesses can fortify their data server’s security defenses.
Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery Strategies
Data loss can have severe consequences for businesses. Data servers provide the capability to perform regular backups and implement disaster recovery strategies. Regular backups ensure that data is copied and stored in a separate location, protecting it from hardware failures, natural disasters, or human errors. In the event of a data loss incident, businesses can restore their data from the backups, minimizing downtime and reducing the impact on operations.
Increasing Efficiency with Data Processing
Data servers are equipped with powerful processors and ample storage, allowing for efficient data processing. By leveraging the processing capabilities of data servers, businesses can perform complex data analytics, data mining, and machine learning tasks, leading to informed decision-making and gaining a competitive edge.
Real-Time Analytics for Instant Insights
Data servers enable businesses to perform real-time analytics, providing instant insights into their operations. Real-time analytics processes data as it is generated, allowing businesses to monitor key metrics, detect trends, and identify opportunities or issues in real-time. This empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions promptly, responding to changing market conditions or customer demands more effectively.
Data Mining for Actionable Intelligence
Data mining involves extracting valuable patterns or knowledge from large datasets. By leveraging the processing power of data servers, businesses can perform data mining techniques, such as clustering, classification, and association analysis, to uncover hidden insights. These insights can then be used to optimize processes, improve customer targeting, or identify new market opportunities.
Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Data servers enable businesses to implement machine learning algorithms, which can analyze large datasets and learn from patterns to make predictions or recommendations. By employing machine learning techniques, businesses can automate tasks, personalize customer experiences, or optimize resource allocation. This enhances efficiency and productivity by reducing manual effort and ensuring more accurate decision-making based on intelligent predictions.
Reducing Downtime with Reliable Data Storage
A robust data server ensures uninterrupted access to critical data, reducing the risk of downtime and minimizing disruptions to business operations. By implementing reliable data storage solutions and measures, businesses can safeguard their data and maintain continuous access to information.
Redundant Storage for Data Availability
Data servers offer various redundant storage options to ensure data availability even in the event of hardware failures. Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) configurations, such as RAID 1 or RAID 5, duplicate data across multiple hard drives, enabling data retrieval in case of drive failures. Additionally, businesses can implement hot-swappable drives, allowing for seamless replacement of failed drives without interrupting operations.
Fault-Tolerant Systems for Continuous Operations
Data servers can be equipped with fault-tolerant systems to ensure continuous operations even in the face of hardware failures. Redundant power supplies, for example, provide backup power in case of a power supply failure. Similarly, redundant network connections or network interface cards (NICs) enable uninterrupted network connectivity. By implementing fault-tolerant systems, businesses can minimize downtime and maintain productivity even when hardware failures occur.
Scalability: Adapting to Changing Business Needs
As businesses grow and evolve, their data storage requirements change as well. Data servers offer scalability options, allowing businesses to easily expand their storage capacity and adapt to changing needs. Scalability ensures that businesses can efficiently manage their data growth without disrupting operations or incurring excessive costs.
Vertical Scalability: Adding Resources to Current Servers
Vertical scalability, also known as scaling up, involves adding resources to existing data servers to meet increased demands. This can be achieved by upgrading hardware components, such as adding more RAM, increasing storage capacity, or installing faster processors. Vertical scalability allows businesses to enhance the performance of their current servers without the need to invest in entirely new infrastructure.
Ngadsen test2
Horizontal Scalability: Adding Additional Servers
Horizontal scalability, or scaling out, involves adding additional data servers to distribute the workload and accommodate growing data needs. This approach ensures that businesses can handle increased data processing and storage requirements by distributing the workload across multiple servers. Horizontal scalability offers flexibility and redundancy, as businesses can add or remove servers as needed, ensuring optimal performance and minimal downtime.
Data servers play a significant role in optimizing network performance by managing data traffic and ensuring efficient data transmission. By implementing features such as load balancing, caching, and content delivery networks (CDNs), businesses can enhance user experience, improve data access speed, and optimize network efficiency. Load balancing is a technique used by data servers to distribute workload evenly across multiple servers or resources. By intelligently allocating incoming data requests, load balancing ensures that no single server is overwhelmed with excessive traffic, minimizing response time and preventing performance bottlenecks. Load balancing also improves fault tolerance, as traffic can be rerouted to healthy servers in case of failures, ensuring uninterrupted service. Data caching is the process of storing frequently accessed data in a cache, reducing the need to retrieve it from the server every time it is requested. By caching data locally, businesses can significantly improve data access speed and reduce network latency. Caching is particularly useful for static or semi-static data that doesn’t change frequently, such as website content or product catalogs. The use of caching reduces the load on the data server, allowing it to focus on processing dynamic or real-time data. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are networks of geographically distributed servers that work together to deliver content to end-users. CDNs store copies of data in multiple locations worldwide, ensuring that data is delivered from the server closest to the user, minimizing latency. By leveraging CDNs, businesses can accelerate data delivery, improve website performance, and enhance user experience, especially for global audiences. Data loss can have catastrophic consequences for businesses. In this section, we will discuss the importance of implementing data backups and disaster recovery strategies using data servers. We will explore different backup methods, recovery options, and the steps businesses can take to minimize the impact of data loss. Regular data backups are essential for protecting critical business data. Data servers enable businesses to automate the backup process, ensuring that data is regularly copied and stored in a separate location. Businesses can choose from various backup methods, such as full backups, incremental backups, or differential backups, depending on their data volume, frequency of changes, and recovery time objectives. By implementing regular backups, businesses can minimize the risk of data loss and ensure that they have a reliable copy of their data in case of emergencies. Storing data backups off-site is crucial for effective disaster recovery. By keeping backups in a separate location from the primary data server, businesses can protect their data from physical damage or localized incidents. Off-site data storage can be achieved through cloud-based backup solutions or by physically transferring backups to a secure location. In the event of a disaster, businesses can restore their data from the off-site backups, ensuring business continuity and minimizing downtime. Having a well-defined and tested disaster recovery plan is essential for minimizing the impact of data loss. Businesses should regularly test their disaster recovery procedures to ensure that data can be successfully restored and that the recovery time objectives are met. It is also crucial to document the disaster recovery plan, including step-by-step instructions, contact information for key personnel, and any additional resources or tools required. By having a comprehensive and tested plan in place, businesses can react swiftly and effectively in the event of a data loss incident. Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way businesses manage their data servers. In this section, we will explore the concept of virtualized data servers, their benefits, and how they enable businesses to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve flexibility. Virtualized data servers involve the abstraction of physical server resources, such as processors, storage, and network, to create multiple virtual servers. These virtual servers can run different operating systems and applications, allowing businesses to consolidate their physical infrastructure and optimize resource utilization. Virtualization offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved flexibility, scalability, and simplified management. Virtualized data servers allow businesses to reduce hardware costs by consolidating multiple virtual servers onto a single physical server. By maximizing resource utilization, businesses can achieve higher efficiency and minimize wasted resources. Virtualization also enables businesses to allocate resources dynamically, ensuring that each virtual server receives the necessary computing power and storage capacity, further optimizing resource usage. Virtualized data servers offer enhanced flexibility and scalability compared to traditional physical servers. With virtualization, businesses can easily add or remove virtual servers based on their changing needs, without the need for additional physical hardware. This allows businesses to adapt quickly to fluctuating workloads or accommodate business growth without incurring excessive costs or disruptions. Managing a virtualized data server environment is often simpler and more efficient than managing multiple physical servers. Virtualization platforms provide centralized management tools that allow businesses to monitor and control all virtual servers from a single interface. This simplifies administrative tasks, such as resource allocation, software updates, and backup management. Additionally, virtualization enables businesses to create isolated environments or test environments easily, further streamlining operations and reducing the time required for deployment. Choosing the right data server is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and meeting the specific needs of your business. In this section, we will provide practical guidance on selecting the right data server, considering factors such as storage capacity, processing power, scalability options, and budget. Assessing your business’s storage capacity requirements is the first step in choosing the right data server. Consider the amount of data your business generates and the expected growth in the coming years. Ensure that the data server you choose offers sufficient storage capacity to meet the current and future needs of your business. Additionally, consider the scalability options of the data server, as your storage requirements may increase over time. Look for servers that offer easy expansion options, such as additional drive bays or compatibility with external storage devices. The processing power of a data server is crucial for efficient data handling and processing. Consider the types of applications and workloads your business will be running on the server. Look for servers with powerful processors and ample RAM to ensure smooth and responsive performance. Consider the number of processor cores and clock speed, as well as the server’s ability to handle simultaneous tasks or virtualization if needed. Scalability is an essential factor when choosing a data server, as it ensures your server can adapt to your business’s changing needs. Consider the server’s expansion capabilities, such as the number of expansion slots or compatibility with future technologies. Future-proofing your data server infrastructure will save your business from costly upgrades or migrations in the future. Look for servers that offer compatibility with emerging technologies or standards, ensuring that your investment remains relevant and usable for years to come. While it is important to consider your budget when choosing a data server, it is equally crucial to evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) over the server’s lifespan. Consider not only the upfront costs but also factors such as power consumption, maintenance, and support costs. Assess the server’s energy efficiency and whether it aligns with your business’s sustainability goals. Additionally, consider the vendor’s reputation, warranty terms, and customer support to ensure a reliable and long-lasting investment. As we conclude our exploration of data servers and their role in streamlining operations, it becomes evident that these powerful tools are essential for businesses seeking enhanced efficiency and productivity. By centralizing data, improving accessibility, ensuring security, and offering scalability, data servers empower organizations to harness the full potential of their data. With the right data server infrastructure in place, businesses can optimize their operations, make informed decisions, and stay ahead in today’s data-driven world. Investing in a reliable and efficient data server is not just a necessity; it is a strategic move that can significantly impact a business’s success. Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, embracing data servers will undoubtedly propel your organization towards greater efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.Load Balancing for Even Work Distribution
Caching for Faster Data Retrieval
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for Faster Data Delivery
Implementing Data Backups and Disaster Recovery
Regular Data Backups for Data Protection
Off-Site Data Storage for Disaster Recovery
Testing and Documenting Disaster Recovery Plans
Streamlining Operations with Virtualized Data Servers
Understanding Virtualized Data Servers
Cost Savings and Improved Resource Utilization
Flexibility and Scalability
Simplified Management and Resource Allocation
Choosing the Right Data Server for Your Business
Evaluating Storage Capacity and Scalability
Assessing Processing Power and Performance
Considering Scalability and Future-Proofing
Budget and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)