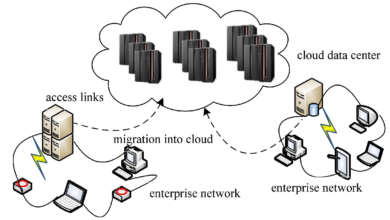
Choosing Best Data Servers
When it comes to managing and storing your valuable data, selecting the right data servers is paramount. The efficiency and reliability of your data infrastructure can significantly impact the performance of your business operations. With a plethora of options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to determine which data servers are best suited for your needs. This comprehensive guide aims to assist you in making an informed decision by providing detailed insights into the key factors to consider when choosing the best data servers for your organization.
Whether you are looking for on-premises solutions or considering cloud-based alternatives, this article will explore various aspects of data servers, including their types, storage capacity, scalability, security features, and more. By understanding the essential attributes of data servers, you will be better equipped to optimize your infrastructure and ensure that your data is safeguarded and readily accessible at all times.
Understanding Different Types of Data Servers
When choosing the best data servers for your organization, it is crucial to understand the different types available in the market. Each type serves a specific purpose and caters to different needs. Here are some of the most common types of data servers:
1. File Servers
File servers are designed to store and manage files and folders. They provide a centralized location for users to access and share files within a network. File servers are ideal for organizations that deal with a large volume of documents, images, videos, and other file types.
2. Database Servers
Database servers are optimized for managing and processing databases. They provide a platform for storing, organizing, and retrieving structured data efficiently. Database servers are essential for businesses that rely heavily on data-driven applications and require fast access to large datasets.
3. Application Servers
Application servers host and execute applications, allowing users to access them remotely. These servers provide the necessary computing resources and services for running complex applications. Application servers are commonly used in enterprise environments where multiple users need access to the same application simultaneously.
4. Web Servers
Web servers handle requests and deliver web pages to users through the internet. They play a crucial role in hosting websites and web applications. Web servers are responsible for processing client requests, retrieving data from databases, and delivering the requested content to the user’s browser.
Understanding the different types of data servers will help you determine which one aligns best with your organization’s needs and requirements.
Evaluating Storage Capacity and Scalability
Storage capacity and scalability are essential considerations when choosing data servers. As your organization grows and generates more data, you need servers that can accommodate your increasing storage needs. Here are some factors to evaluate in terms of storage capacity and scalability:
1. RAID Configurations
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations determine how data is distributed and protected across multiple drives. There are different RAID levels, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10, each offering varying levels of performance, redundancy, and capacity. Assess the RAID options available in data servers to ensure optimal data protection and storage efficiency.
2. Drive Types
The type of drives used in data servers can impact their storage capacity and performance. Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) offer larger storage capacities but are generally slower compared to solid-state drives (SSDs). SSDs provide faster data access and transfer speeds, making them ideal for applications that require high-performance storage. Consider the trade-offs between capacity and performance when selecting the drive types for your data servers.
3. Expansion Options
As your data storage needs grow, it is essential to have expansion options available in your data servers. Look for servers that offer expandable drive bays or support additional external storage devices. This flexibility allows you to scale your storage capacity seamlessly without disrupting your operations.
Evaluating storage capacity and scalability ensures that your data servers can handle your current and future data storage requirements efficiently.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Data security is a crucial consideration when selecting data servers. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats is paramount. Here are some key security features to look for:
1. Encryption
Encryption is the process of encoding data to make it unreadable to unauthorized individuals. Look for data servers that offer strong encryption mechanisms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
2. Access Controls
Effective access controls enable you to manage user permissions and restrict access to sensitive data. Look for data servers that offer robust access control mechanisms, including user authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and granular permission settings.
3. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Data servers should have built-in firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to protect against unauthorized network access and malicious activities. These security measures help safeguard your data from external threats, such as hackers or malware.
4. Physical Security
Consider the physical security measures implemented in the data server environment. Features like locked server rooms, video surveillance, and access logs can enhance the overall security of your data infrastructure.
Ensuring data security and privacy is vital to protect your organization’s sensitive information and maintain compliance with data protection regulations.
Analyzing Performance and Reliability
Performance and reliability are critical factors to consider when selecting data servers. Here are some key aspects to analyze:
1. Processing Power
The processing power of data servers determines their ability to handle computational tasks efficiently. Look for servers with powerful processors that can handle your workload requirements without experiencing performance bottlenecks.
2. Memory Capacity
Ample memory capacity is essential for data servers to handle multiple concurrent requests and process large datasets effectively. Evaluate the memory specifications of servers to ensure they can meet your performance needs.
3. Disk Speed
The speed at which data can be read from or written to the disk impacts overall server performance. Consider data servers with high-speed disks, whether HDDs or SSDs, to minimize data access and transfer latency.
4. Redundancy and Uptime
Redundancy features, such as redundant power supplies and RAID configurations, enhance the reliability of data servers. Look for servers that offer high availability and ensure minimal downtime to prevent disruptions to your business operations.
By thoroughly analyzing the performance and reliability aspects of data servers, you can select servers that meet your organization’s performance requirements and deliver consistent and dependable service.
Considering On-Premises vs. Cloud-Based Solutions
When choosing data servers, you have the option to either deploy on-premises servers within your organization or opt for cloud-based solutions. Consider the following factors when deciding between these options:
1. Cost Implications
On-premises data servers typically involve significant upfront costs, including server hardware, networking equipment, and infrastructure setup. Cloud-based solutions, on the other hand, often operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing you to allocate resources based on your needs and budget. Consider your organization’s financial capabilities and long-term cost projections to make an informed decision.
2. Maintenance and Support
On-premises data servers require regular maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting. This responsibility falls on your organization’s IT staff or external service providers. Cloud-based solutions, on the other hand, often come with managed services, where the cloud provider handles maintenance and support tasks. Assess your organization’s IT capabilities and resources when considering the maintenance aspect.
3. Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud-based solutions offer greater flexibility and scalability compared to on-premises servers. With cloud servers, you can easily scale your resources up or down based on demand, allowing for efficient resource allocation. On-premises servers require careful planning and investments for future scalability. Consider your organization’s growth projections and resource requirements to determine which option offers the necessary flexibility.
4. Data Privacy and Compliance
Data privacy and compliance requirements vary across industries and regions. Evaluate the data privacy implications of both on-premises and cloud-based solutions. On-premises servers provide more control over your data, while cloud solutions may be subject to specific regulations and certifications. Ensure that your chosen solution aligns with your organization’s data privacy and compliance needs.
By considering the cost implications, maintenance requirements, flexibility, and data privacy aspects, you can make an informed decision about deploying on-premises servers or opting for cloud-based data server solutions.
Assessing Disaster Recovery and Backup Options
Disaster recovery and backup solutions are crucial for safeguarding your data and ensuring business continuity in the event of a system failure or data loss. Consider the following aspects when assessing disaster recovery and backup options:
Ngadsen test2
1. Replication
Replication involves creating and maintaining copies of your data in multiple locations. This ensures that if one server or location fails, you can quickly switch to a replicated copy and continue operations without significant disruptions. Evaluate data servers that offer built-in replicationcapabilities or consider implementing replication strategies using third-party software or cloud-based services.
2. Snapshots
Snapshots allow you to capture a point-in-time image of your data, including its configurations and settings. These snapshots can be used to restore your data to a specific state in case of data corruption or accidental deletion. Look for data servers that support snapshot functionality or consider implementing snapshot-based backup solutions.
3. Off-Site Backups
Off-site backups involve storing copies of your data in a separate physical location or on a different cloud provider’s infrastructure. This ensures that your data remains safe even if your primary data server location is affected by a disaster. Evaluate backup options that allow for off-site storage and consider the frequency and efficiency of data synchronization between your primary and backup locations.
4. Testing and Recovery Procedures
Regularly test your disaster recovery and backup procedures to ensure their effectiveness. Conduct simulated disaster scenarios to verify the integrity and accessibility of your backup data. Document and maintain a clear recovery plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a system failure or data loss.
By assessing disaster recovery and backup options, you can establish robust strategies to protect your data and minimize the impact of unforeseen events.
Evaluating Cost-Effectiveness and Return on Investment
Choosing the best data servers involves evaluating their cost-effectiveness and assessing the return on investment (ROI) they can provide for your organization. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) of data servers, which includes not only the initial hardware and software costs but also ongoing expenses such as maintenance, energy consumption, and upgrades. Evaluate the long-term financial implications of different server options to ensure they align with your budget and resource allocation.
2. Scalability and Future Growth
Factor in the scalability of data servers and their ability to accommodate your organization’s future growth. Investing in servers that can scale with your business can help avoid the need for frequent hardware upgrades or replacements, resulting in cost savings in the long run.
3. Performance and Efficiency
Consider the performance and efficiency of data servers in relation to their cost. While high-performance servers may come with a higher price tag, they can deliver better processing speeds and improved resource utilization, resulting in optimized productivity and operational efficiency.
4. ROI Calculation
Calculate the potential return on investment (ROI) of your chosen data servers. Take into account factors such as increased productivity, reduced downtime, improved data accessibility, and enhanced security. Compare the projected benefits with the associated costs to determine the overall value and ROI of your server investment.
By evaluating the cost-effectiveness and ROI of data servers, you can make informed decisions that align with your organization’s financial goals and objectives.
Understanding Virtualization and Containerization
Virtualization and containerization technologies offer significant benefits in terms of resource utilization, flexibility, and scalability. Here’s a closer look at these concepts:
1. Virtualization
Virtualization allows you to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. Each VM operates as a separate entity, allowing for efficient utilization of hardware resources. Virtualization enables you to consolidate your server infrastructure, leading to cost savings on hardware, power, and maintenance. Evaluate data servers that support virtualization technologies, such as hypervisors, and consider the potential benefits of consolidating your infrastructure through virtualization.
2. Containerization
Containerization is a lightweight alternative to traditional virtualization. Containers provide isolated environments for running applications, enabling efficient resource allocation and portability. Containers share the host operating system, resulting in reduced overhead and faster application deployment. Investigate data servers that support containerization technologies, like Docker, and explore the advantages of containerizing your applications for improved scalability and flexibility.
3. Benefits and Considerations
Both virtualization and containerization offer benefits such as improved resource utilization, simplified infrastructure management, and faster application deployment. However, it is essential to consider factors like security, performance overhead, and compatibility when adopting these technologies. Assess your organization’s specific needs and evaluate the potential advantages and challenges associated with virtualization and containerization.
Understanding virtualization and containerization technologies can help optimize the utilization of your data servers and enhance the efficiency of your infrastructure.
Exploring Hybrid Data Server Solutions
Hybrid data server solutions combine the benefits of both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructures. Here’s why you should consider hybrid solutions:
1. Increased Reliability
Hybrid solutions offer increased reliability by utilizing both on-premises and cloud resources. In the event of a local server failure, critical workloads can be seamlessly shifted to the cloud, ensuring uninterrupted operations and minimizing downtime.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Hybrid solutions provide the scalability and flexibility to accommodate changing resource requirements. You can scale your on-premises infrastructure for predictable workloads while leveraging the cloud for unpredictable or bursty workloads. This flexibility allows you to optimize resource allocation and control costs.
3. Cost Optimization
Hybrid solutions allow you to optimize costs by leveraging the cost-effectiveness of on-premises infrastructure for specific workloads while utilizing the scalability and pay-as-you-go model of the cloud for others. This hybrid approach can result in significant cost savings compared to a fully on-premises or fully cloud-based infrastructure.
4. Data Control and Compliance
Hybrid solutions provide organizations with greater control over their data. Certain regulations or internal policies may require sensitive data to be stored on-premises, while other data can be stored in the cloud. Hybrid solutions allow you to maintain compliance and meet data governance requirements.
Consider implementing hybrid data server solutions to leverage the advantages of both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructures, resulting in increased reliability, scalability, and cost optimization.
Considering Future Growth and Technological Advancements
When selecting data servers, it is essential to consider future growth and technological advancements. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
1. Anticipating Future Growth
Assess your organization’s growth projections and evaluate whether the chosen data servers can scale to meet future requirements. Consider factors such as increasing data volumes, expanding user base, and emerging business needs. Future-proofing your infrastructure ensures that you can accommodate growth without significant disruptions or costly infrastructure upgrades.
2. Emerging Technologies
Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends that may impact data servers. For example, edge computing, which brings compute resources closer to the data source, can improve latency and responsiveness for certain applications. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can also impact data processing and analytics requirements. Understanding these advancements can help you select data servers that can support and leverage these technologies in the future.
3. Scalable and Adaptable Infrastructure
Invest in data servers that offer scalability, adaptability, and compatibility with evolving technologies. Look for servers that support modular designs, allowing for easy upgrades and integration with new technologies. An infrastructure that can accommodate future advancements ensures that your organization remains competitive and agile in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Considering future growth and technological advancements when selecting data servers enables you to build a robust infrastructure that can adapt to changing needs and leverage emerging technologies for a competitive advantage.
In conclusion, choosing the best data servers for your organization is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. By understanding the different types of data servers, evaluating storage capacity and scalability, prioritizing data security, considering performance and reliability, and exploring different deployment options, you can optimize your infrastructure and enhance your business operations. Additionally, assessing disaster recovery options, cost-effectiveness, virtualization technologies, and future growth potential will contribute to making an informed choice that aligns with your organization’s needs. Remember, selecting the right data servers is a crucial step towards ensuring the integrity, accessibility, and efficiency of your valuable data.