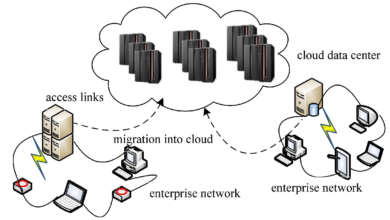
Cloud Data Server Evolution
In today’s digital landscape, the evolution of cloud data servers has revolutionized the way businesses store, manage, and access their data. From their humble beginnings as physical servers to the modern-day cloud infrastructure, this article will delve into the fascinating journey of cloud data servers. We will explore the key milestones, technological advancements, and the impact they have had on the world of data storage and management.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover everything from the early stages of data server development to the emergence of virtualization and the advent of cloud computing. Each section will provide a detailed analysis of the significant breakthroughs and innovations that have shaped the evolution of cloud data servers.
The Birth of Data Servers
The birth of data servers marked a significant turning point in the digital age. In the 1950s, as businesses began to recognize the immense value of data, the need for efficient storage and management solutions became apparent. This led to the development of the first data servers, which were physical machines designed to store and process data.
Early data servers were large, expensive, and limited in capacity. They relied on magnetic tape storage systems and lacked the processing power we take for granted today. However, these initial machines laid the groundwork for future advancements in data storage and set the stage for the evolution of cloud data servers.
The Rise of Centralized Data Centers
As technology progressed, the demand for more efficient data storage solutions grew. This resulted in the rise of centralized data centers, which housed multiple data servers in a single location. These data centers provided a more scalable and cost-effective solution for businesses, allowing them to store and manage larger volumes of data.
The concept of centralized data centers revolutionized the way businesses handled their data. It allowed for better organization and improved accessibility, as data could be stored in a central location and accessed by authorized personnel. This marked a significant step towards the modern-day cloud infrastructure we know today.
The Emergence of Networked Data Servers
As businesses expanded their operations and required data access from multiple locations, the need for networked data servers became apparent. This led to the development of local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs), which allowed for the seamless sharing of data between different servers and locations.
Networked data servers brought about a new level of efficiency and collaboration. Businesses could now access and share data across their organization, improving communication and decision-making processes. This was a crucial milestone in the evolution of data servers, as it laid the foundation for the interconnectedness we see in cloud data servers today.
The Rise of Virtualization
Virtualization marked a significant milestone in the evolution of data servers. It introduced the concept of virtual machines (VMs), which allowed multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server. This breakthrough technology revolutionized data server efficiency, utilization, and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of Virtualization
Virtualization brought numerous advantages to data server management. Firstly, it allowed businesses to consolidate their physical server infrastructure, reducing the need for multiple machines and saving on hardware costs.
Secondly, virtualization improved server utilization by allowing for the efficient allocation of resources. With the ability to run multiple VMs on a single server, businesses could maximize their computing power and storage capacity, resulting in better performance and cost savings.
Popular Virtualization Technologies
Several virtualization technologies emerged over the years, each with its own unique features and benefits. One of the most popular virtualization platforms is VMware, which provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing virtualized environments.
Another notable technology is Xen, an open-source hypervisor that offers high performance and flexibility. Xen has gained popularity in the cloud computing industry, as it allows for the efficient allocation of resources and supports a wide range of operating systems.
The Emergence of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing marked a paradigm shift in the way organizations store and handle their data. It brought about a new era of flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, making it the go-to solution for businesses of all sizes.
Defining Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be defined as the delivery of computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, software, and analytics, over the internet. Rather than owning and maintaining physical servers, businesses can access these resources on-demand from cloud service providers.
Cloud computing offers several deployment models, including public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud. Each model provides a different level of control, security, and scalability, allowing businesses to choose the option that best suits their needs.
The Benefits of Cloud Data Servers
Cloud data servers bring numerous benefits to businesses, transforming the way they store and manage their data. One of the key advantages is scalability. With cloud data servers, businesses can easily scale their storage and processing capabilities as their data needs grow. This eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades and provides a flexible solution that can adapt to changing demands.
Another benefit is cost-effectiveness. Cloud data servers operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to only pay for the resources they use. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, making cloud data servers an attractive option for businesses with limited budgets.
Scalability and Elasticity: Handling Data Demands
One of the most significant advantages of cloud data servers is their ability to scale and adapt to changing data demands. This section will explore the scalability and elasticity features offered by cloud data servers and how businesses can leverage them to meet their evolving needs.
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as scaling up, involves adding more resources to an existing server to increase its capacity. With cloud data servers, businesses can easily scale vertically by upgrading the resources allocated to their virtual machines. This includes increasing the CPU power, memory, or storage capacity of a server.
This form of scaling is ideal for businesses that experience sudden spikes in data demands. By vertically scaling their cloud data servers, they can quickly accommodate the increased workload without any disruption to their operations.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more servers to distribute the workload and increase overall capacity. Cloud data servers excel in horizontal scaling, as businesses can easily spin up additional virtual machines to handle the increased data demands.
Horizontal scaling offers several benefits, including improved performance and fault tolerance. By distributing the workload across multiple servers, businesses can handle higher traffic loads without compromising on speed or reliability. Additionally, if one server fails, the workload can be seamlessly shifted to the remaining servers, ensuring uninterrupted service.
Elasticity
Elasticity is a key feature of cloud data servers that allows businesses to dynamically adjust their resource allocation based on real-time demands. With elastic cloud data servers, businesses can automatically scale up or down in response to changes in workload, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
For example, during periods of high traffic, elastic cloud data servers can automatically allocate additional resources to handle the increased load. Conversely, during periods of low traffic, resources can be scaled back to minimize costs. This flexibility provides businesses with the agility they need to adapt to fluctuating demands and optimize their data server performance.
Security and Data Protection
Data security is a paramount concern for businesses, especially when it comes to storing sensitive information on cloud data servers. This section will explore the security measures implemented by cloud data servers to safeguard data and protect against unauthorized access or data breaches.
Data Encryption
Encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data stored on cloud data servers. Cloud service providers implement robust encryption algorithms to encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
During transit, data is encrypted using secure protocols such as SSL/TLS, ensuring that it remains protected as it travels between the user’s device and the cloud server. At rest, data is encrypted using encryption keys, making it unreadable to anyone without the proper authorization.
Access Controls and Authentication
Cloud data servers employ strict access controls and authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized individuals can access stored data. This includes implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC).
RBAC allows businesses to define granular access permissions for different users or user groups. This ensures that only those with the necessary privileges can access or modify sensitive data. Additionally, audit logs are maintained to track and monitor user activities, providing an additional layer of security and accountability.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud data servers offer robust data backup and disaster recovery capabilities, allowing businesses to protect their data from loss or corruption. Regular backups are performed to ensure that data can be restored in the event of accidental deletion, hardware failure, or natural disasters.
Cloud service providers often offer backup options such as snapshots or automated backup schedules, allowing businesses to choose the level of data protection that suits their needs. In addition to backups, disaster recovery plans are in place to ensure that businesses can quickly recover their data and resume operations in the event of a catastrophic event.
High Availability and Redundancy
High availability and redundancy are essential aspects of cloud data servers, ensuring that businesses experience minimal downtime and data loss. This section will explorethe concepts of high availability and redundancy, and how they are implemented in cloud data servers to maintain uninterrupted service and data integrity.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is a technique used in cloud data servers to evenly distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers. By distributing the workload, load balancing ensures optimal resource utilization and prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed.
Load balancers monitor the performance and availability of servers and direct incoming requests to the most suitable server based on factors such as server capacity, response time, and current workload. This not only improves the overall performance of the data server infrastructure but also enhances fault tolerance by preventing any single point of failure.
Failover and Redundancy
Failover and redundancy mechanisms play a vital role in ensuring high availability and data protection in cloud data servers. Failover refers to the automatic transfer of operations from a failed server to a backup server to maintain uninterrupted service.
Cloud data servers employ various failover mechanisms, such as clustering or replication, to ensure that if one server fails, another server seamlessly takes over the workload. This redundancy ensures that businesses can continue their operations without experiencing significant downtime or data loss.
Data Replication and Mirroring
Data replication and mirroring are techniques used to create redundant copies of data across multiple servers or locations. By replicating data, cloud data servers provide an added layer of protection against hardware failures or data corruption.
In the event of a server failure, data can be retrieved from the replicated copies, ensuring that businesses can access their data without disruption. Additionally, data mirroring allows for real-time synchronization of data between primary and backup servers, ensuring that any changes made to the primary server are immediately replicated to the backup server.
Hybrid Cloud: The Best of Both Worlds
The hybrid cloud model combines the benefits of public and private cloud deployments, offering businesses a flexible and customizable solution for their data storage needs. This section will explore the concept of hybrid cloud and how it allows organizations to strike a balance between security, cost-efficiency, and scalability.
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
A public cloud refers to a cloud infrastructure that is shared among multiple users and hosted by a cloud service provider. It offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of management, making it an attractive option for businesses with varying data storage needs.
Ngadsen test2
On the other hand, a private cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure solely used by a single organization. It offers enhanced security, control, and customization options, making it ideal for businesses with strict compliance requirements or sensitive data.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud model combines the advantages of both public and private clouds, allowing businesses to optimize their data storage strategy. With hybrid cloud, organizations can store sensitive or critical data in a private cloud for enhanced security, while leveraging the scalability and cost-efficiency of public cloud services for other non-sensitive data.
Hybrid cloud also provides businesses with the flexibility to scale their data storage based on changing requirements. During periods of high demand, businesses can seamlessly extend their storage capabilities to the public cloud, ensuring that they have the necessary resources without investing in additional infrastructure.
Edge Computing: Bringing Data Closer
Edge computing has gained prominence in recent years, enabling data processing closer to the source. This section will explain how edge computing enhances the performance and responsiveness of cloud data servers, particularly in scenarios where low latency is crucial.
The Concept of Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing and analyzing data at or near the source of data generation, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud server for processing. This decentralized approach reduces latency and improves response times, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data analysis or low-latency interactions.
Edge computing is commonly used in scenarios such as IoT (Internet of Things), where data is generated by sensors or devices located in remote or distributed environments. By processing data at the edge, businesses can make faster and more informed decisions, without relying on a centralized cloud infrastructure.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several benefits for cloud data servers. Firstly, it reduces network congestion and bandwidth requirements by processing data locally. This results in faster response times and improved user experiences, particularly for applications that require real-time interactions or data analysis.
Secondly, edge computing enhances data privacy and security. Since data is processed locally, it reduces the risk of sensitive information being transmitted over the network or stored in a centralized cloud server. This is especially important in industries with strict compliance regulations or where data confidentiality is paramount.
The Future of Cloud Data Servers
As technology continues to advance, the future of cloud data servers holds exciting possibilities. This section will explore emerging trends such as serverless computing, artificial intelligence integration, and the potential impact of quantum computing on data server architecture.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), is an emerging trend in cloud data servers. With serverless computing, businesses can run applications without the need to manage or provision servers. Instead, they can focus on writing and deploying code in the form of functions, which are triggered by specific events or requests.
Serverless computing offers several advantages, including cost savings, scalability, and reduced operational complexity. It allows businesses to pay only for the actual execution time of their functions, eliminating the need for idle server resources. Additionally, serverless computing can automatically scale to handle high traffic loads, ensuring optimal performance without the need for manual intervention.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with cloud data servers is another exciting development on the horizon. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, can be leveraged to analyze and extract insights from vast amounts of data.
Cloud data servers provide the necessary resources and scalability to train and deploy AI models. By combining the power of cloud computing with AI, businesses can unlock valuable insights, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Quantum Computing and Data Server Architecture
Quantum computing holds enormous potential for revolutionizing the field of data server architecture. Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations at an unprecedented speed, far surpassing the capabilities of traditional computers.
While quantum computing is still in its early stages, it has the potential to significantly impact data server architecture. Quantum computers could offer enhanced encryption capabilities, enabling more robust security measures for cloud data servers. Additionally, quantum computing algorithms could optimize data storage and processing, opening up new possibilities for managing and analyzing massive datasets.
Choosing the Right Cloud Data Server Solution
With a plethora of options available, selecting the right cloud data server solution can be a daunting task. This section will provide guidance on factors to consider when choosing a cloud data server provider, including performance, cost, security, and scalability. We will also discuss different service models, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Performance and Scalability
When evaluating cloud data server solutions, performance and scalability should be key considerations. Businesses should assess the provider’s infrastructure, network capabilities, and track record in delivering reliable and high-performance services. They should also ensure that the solution can scale seamlessly to accommodate their data growth and evolving needs.
Cost and Pricing Models
Cost is a crucial factor when selecting a cloud data server solution. Businesses should carefully evaluate the pricing models offered by different providers, considering factors such as the cost per storage, data transfer, and compute resources. They should also consider any additional charges, such as data retrieval or backup fees, to accurately assess the total cost of ownership.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security should be a top priority when choosing a cloud data server solution. Businesses should inquire about the provider’s security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications. They should ensure that the provider adheres to industry standards and regulations, particularly if they handle sensitive or regulated data.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define the level of service and support that businesses can expect from their cloud data server provider. Businesses should carefully review the SLA terms, including uptime guarantees, response times for support requests, and compensation mechanisms in case of service disruptions. SLAs provide businesses with assurance and recourse should any issues arise.
IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS?
Cloud data server solutions come in various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Businesses should assess their specific requirements and determine which service model best aligns with their needs.
IaaS offers businesses greater control and flexibility, allowing them to manage the underlying infrastructure and deploy their own applications. PaaS provides a more streamlined approach, offering preconfigured platforms and frameworks for developing and deploying applications. SaaS, on the other hand, offers ready-to-use software applications, reducing the need for in-house development and management.
In conclusion, the evolution of cloud data servers has revolutionized the way businesses handle their data, offering unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and security. From the early days of physical servers to the emergence of virtualization and cloud computing, the journey of data servers has been marked by significant breakthroughs and innovationsthat have transformed the way organizations store, manage, and harness the power of their data. With the rise of virtualization, businesses gained the ability to consolidate their server infrastructure, improve resource utilization, and reduce costs. The emergence of cloud computing further expanded these benefits, providing businesses with on-demand access to scalable resources, cost-effective pricing models, and the ability to leverage advanced technologies.
The scalability and elasticity features of cloud data servers have been instrumental in handling the ever-growing data demands of businesses. Vertical scaling allows businesses to add more resources to existing servers, increasing their capacity to handle larger workloads. This scalability is ideal for businesses experiencing sudden spikes in data demands, as they can quickly and efficiently allocate additional resources to meet the increased workload.
Horizontal scaling, on the other hand, involves adding more servers to distribute the workload and increase overall capacity. By distributing the workload across multiple servers, businesses can achieve better performance, improved fault tolerance, and the ability to handle higher traffic loads without compromising on speed or reliability. The elasticity of cloud data servers allows for the automatic scaling up or down of resources based on real-time demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Data security and protection are critical considerations when utilizing cloud data servers. Encryption is a fundamental aspect of data security, ensuring that data remains confidential and intact during transit and at rest. Robust access controls and authentication mechanisms are implemented to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. Data backup and disaster recovery strategies are also essential to safeguard against data loss and ensure business continuity in the face of unforeseen events.
High availability and redundancy are key features of cloud data servers to minimize downtime and data loss. Load balancing techniques evenly distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, optimizing resource utilization and preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. Failover mechanisms and data replication ensure uninterrupted service by automatically transferring operations to backup servers in the event of a failure. These redundancy measures provide businesses with the confidence that their data will remain accessible and protected.
The hybrid cloud model combines the benefits of public and private clouds, allowing businesses to tailor their data storage strategy to their specific needs. Sensitive or critical data can be stored in a private cloud for enhanced security and control, while non-sensitive data can be stored in a public cloud for scalability and cost-effectiveness. The hybrid cloud provides businesses with the flexibility to scale their data storage based on changing requirements and optimize their cost-efficiency.
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving response times. By processing data locally, businesses can achieve real-time data analysis, low-latency interactions, and enhanced data privacy and security. Edge computing is particularly valuable in scenarios where immediate insights or actions are required, such as IoT applications or real-time analytics.
Looking towards the future, cloud data servers are poised to continue evolving and adapting to technological advancements. Serverless computing, with its focus on function-based architecture, offers businesses greater agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The integration of artificial intelligence into cloud data servers enables advanced data analysis, automation, and decision-making. Quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize data server architecture, offering enhanced encryption capabilities and unlocking new possibilities for data storage and processing.
When selecting a cloud data server solution, businesses should consider factors such as performance, scalability, cost, security, and service level agreements (SLAs). They should assess their specific requirements and choose the service model that aligns best with their needs, whether it be IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS. Careful evaluation and consideration of these factors will ensure that businesses choose a cloud data server solution that meets their operational and strategic objectives.
In conclusion, the evolution of cloud data servers has transformed the way businesses store, manage, and access their data. From the birth of data servers to the rise of virtualization and the emergence of cloud computing, each stage has brought new capabilities, improved efficiency, and enhanced security. As technology continues to advance, the future of cloud data servers holds exciting possibilities, allowing businesses to harness the power of scalability, flexibility, and advanced technologies to drive innovation and success in the digital age.