Cost-Effective Data Server Strategies
In today’s digital era, data has become the lifeblood of businesses across all industries. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, having a robust and reliable data server infrastructure is crucial for smooth operations and optimal performance. However, setting up and maintaining a powerful data server can often come with a hefty price tag, making it a daunting task for organizations with limited resources.
In this blog article, we will explore cost-effective strategies that can help businesses optimize their data server infrastructure without compromising on performance or security. From leveraging cloud solutions to implementing efficient data management techniques, we will delve into various approaches that can significantly reduce costs while maximizing efficiency.
Embracing Cloud Computing: A Game-Changer for Cost Optimization
Summary: Explore the benefits of cloud computing and how it can revolutionize data server strategies, including cost savings, scalability, and enhanced flexibility.
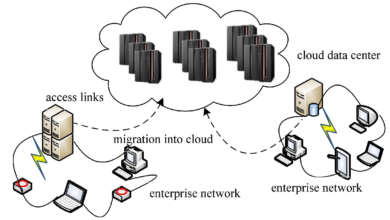
Cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for businesses seeking cost-effective data server solutions. With cloud services, organizations can leverage the infrastructure and resources provided by cloud service providers, eliminating the need for extensive on-premises server setups. This shift to the cloud not only reduces upfront hardware costs but also eliminates the need for ongoing maintenance and upgrades, resulting in significant long-term savings.
One key advantage of cloud computing is its scalability. Cloud platforms allow businesses to easily scale their server resources based on their current needs. Whether it’s a sudden influx of data or an increase in user traffic, cloud services can quickly adapt to accommodate changing demands. This scalability eliminates the need for overprovisioning hardware, effectively reducing costs associated with underutilized resources.
Public vs. Private Cloud
When considering cloud computing for data servers, businesses have the option to choose between public and private cloud solutions. Public clouds, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, offer cost-effective pay-as-you-go models, where organizations only pay for the resources they consume. On the other hand, private clouds provide dedicated resources for a single organization, offering increased control and security but at a higher cost. Businesses must assess their specific requirements and budget constraints to determine the most suitable cloud deployment model.
Hybrid Cloud Approach
For organizations seeking the best of both worlds, a hybrid cloud approach can be a viable solution. Hybrid cloud combines the use of both public and private clouds, allowing businesses to leverage the cost savings and scalability of public cloud services while maintaining sensitive data in a private cloud environment. This approach offers flexibility and cost optimization, as businesses can allocate non-sensitive data to the public cloud, reducing infrastructure costs, while ensuring the security and compliance of critical data in their private cloud.
Virtualization: Consolidating Workloads for Efficiency and Savings
Summary: Learn how virtualization technologies can enable businesses to optimize server resources, reduce hardware costs, and increase overall efficiency.
Virtualization technology has revolutionized data server strategies, allowing businesses to consolidate multiple workloads onto a single physical server. By separating the physical hardware from the software, virtualization enables efficient utilization of server resources, leading to significant cost savings.
With virtualization, organizations can create multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, each running its own operating system and applications. This consolidation eliminates the need for separate physical servers for each workload, reducing hardware costs, space requirements, and power consumption. Additionally, virtualization allows for efficient resource allocation, as server resources can be dynamically allocated and shared among multiple VMs based on their needs, ensuring optimal utilization and minimizing wastage.
Hypervisor Technology
A key component of virtualization is the hypervisor, which is responsible for creating and managing virtual machines. There are two types of hypervisors: Type 1, also known as bare-metal hypervisors, run directly on the server hardware, providing direct access to hardware resources. Type 2 hypervisors, on the other hand, run on top of an existing operating system. Each type has its advantages and considerations, and businesses must choose the most suitable hypervisor based on their specific requirements.
Containerization
Another virtualization technology gaining popularity is containerization, which allows for the creation and deployment of lightweight, isolated containers that run applications and their dependencies. Containers provide a more efficient alternative to traditional VMs, as they share the host operating system kernel, eliminating the need for a separate guest operating system for each container. This reduces resource overhead and enables faster startup times and greater scalability. Containerization can be particularly beneficial in scenarios where rapid deployment and scalability are critical, contributing to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Implementing Data Deduplication: Minimizing Redundancy, Maximizing Savings
Summary: Discover the concept of data deduplication and its impact on reducing storage requirements, ultimately leading to significant cost savings.
Data deduplication is a technique used to eliminate duplicate copies of data, significantly reducing storage requirements and associated costs. By identifying and removing redundant data, businesses can optimize their storage infrastructure and achieve substantial savings in both hardware and operational expenses.
There are two primary approaches to data deduplication: file-level and block-level deduplication. File-level deduplication identifies duplicate files and stores only a single copy, regardless of the number of instances across the storage system. Block-level deduplication, on the other hand, breaks data into smaller blocks and compares them for redundancy, storing only unique blocks and referencing duplicate blocks as needed. Both methods have their advantages and considerations, and organizations must evaluate their data characteristics and storage requirements to determine the most suitable deduplication approach.
Inline vs. Post-Process Deduplication
When implementing data deduplication, businesses must also consider the timing of the deduplication process. Inline deduplication occurs in real-time as data is written to storage, immediately identifying and eliminating duplicates before they are stored. This approach minimizes storage requirements from the outset but may introduce latency during the write process. Post-process deduplication, on the other hand, performs deduplication as a background process, allowing data to be written first and then identifying duplicates afterward. While post-process deduplication may require more storage initially, it avoids potential write performance impacts. Organizations must weigh the trade-offs and select the most appropriate deduplication method based on their specific needs.
Utilizing Server Colocation: Sharing Costs, Maximizing Reliability
Summary: Explore the benefits of server colocation, including reduced infrastructure costs, enhanced reliability, and improved disaster recovery capabilities.
Server colocation offers businesses the opportunity to house their data servers in a third-party data center, sharing costs with other organizations while enjoying enhanced reliability and disaster recovery capabilities. By colocating their servers, businesses can reduce infrastructure costs, optimize resource utilization, and focus on their core competencies without the burden of managing a physical data center.
One primary advantage of server colocation is the cost savings it offers. Instead of investing in building and maintaining their own data center, businesses can lease space in a colocation facility. This eliminates the need for upfront capital expenditure and ongoing operational costs associated with power, cooling, and maintenance. Additionally, colocation providers often benefit from economies of scale, allowing businesses to access enterprise-grade infrastructure and redundant network connectivity at a fraction of the cost of building and managing their own facility.
Physical Security and Redundancy
Colocation facilities prioritize physical security, offering robust measures such as access controls, surveillance systems, and 24/7 monitoring to protect the servers housed within. These security measures ensure the safety and integrity of critical data, providing peace of mind to businesses. Furthermore, colocation facilities typically have redundant power and cooling systems, minimizing the risk of downtime due to power outages or environmental factors. Redundant network connectivity is also a common feature, providing high availability and minimizing the impact of network failures.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Colocation facilities often offer comprehensive disaster recovery solutions, including redundant backups, data replication, and failover capabilities. By colocating their servers in geographically diverse locations, businesses can ensure that their data is protected against natural disasters, human errors, or other unforeseen events. In the event of a disaster, colocation facilities can swiftly restore services and minimize downtime, enabling businesses to maintain continuity and prevent data loss.
Automation: Streamlining Processes for Efficiency and Productivity
Summary: Learn how automation tools can help businesses eliminate manual tasks, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately reduce operational costs.
Automation has become a powerful tool in optimizing data server strategies, enabling businesses to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs associated with manual labor. By automating repetitive tasks and workflows, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively and focus on strategic initiatives.
One area where automation can have a significant impact is server provisioning and configuration management. Instead of manually deploying and configuring servers, businesses can leverage infrastructure-as-code solutions, such as Ansible or Terraform, to define server configurations and automate the provisioning process. This not only eliminates human error but also accelerates server deployment, enabling faster time-to-market for new services or applications.
Monitoring and Alerting Automation
Automated monitoring and alerting systems can provide real-time insights into the health and performance of data servers. By continuously monitoring key metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic, businesses can proactively identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and prevent potentialissues before they escalate. Automated alerts can notify IT teams of any anomalies or potential issues, allowing for prompt resolution and minimizing downtime. By automating these monitoring and alerting processes, businesses can improve server performance, reduce the need for manual intervention, and ultimately save on operational costs.
Backup and Recovery Automation
Automating backup and recovery processes is crucial for ensuring data protection and minimizing the risk of data loss. By implementing automated backup solutions, businesses can schedule regular backups, eliminate the dependence on manual backups, and reduce the chances of human error. Additionally, automated recovery processes can expedite the restoration of data in the event of a failure or disaster, minimizing downtime and improving business continuity. By leveraging automation for backup and recovery, organizations can optimize data server strategies, enhance data protection, and reduce the costs associated with manual backup and recovery efforts.
Data Tiering: Optimizing Storage Costs Based on Access Frequencies
Summary: Discover the concept of data tiering and how businesses can strategically allocate data across different storage tiers to achieve cost-effective storage solutions.
Data tiering involves categorizing data based on its access frequency and storing it on different storage tiers accordingly. By implementing data tiering strategies, businesses can optimize storage costs by allocating less frequently accessed data to more cost-effective storage solutions while ensuring that frequently accessed data remains readily available on high-performance storage.
Ngadsen test2
One common approach to data tiering is hierarchical storage management (HSM), which involves moving data between different storage tiers based on predefined policies. Frequently accessed or critical data can reside on high-performance storage, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), for fast access times. Less frequently accessed data can be moved to lower-cost storage options, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) or even tape storage, which provides cost-effective long-term retention.
Data Classification and Policies
Implementing data tiering requires classifying data based on its access patterns and defining policies for data movement between tiers. Data classification can be based on factors such as usage patterns, business relevance, or regulatory requirements. By understanding the characteristics of the data and its access patterns, businesses can determine the most suitable storage tiers for each category, ensuring cost-effective storage while maintaining performance requirements.
Automated Data Movement
To streamline the data tiering process, businesses can leverage automated data movement tools or storage systems that offer built-in tiering capabilities. These tools can automatically move data between storage tiers based on predefined policies, ensuring that data is in the appropriate tier at all times. Automated data movement reduces the need for manual intervention, improves operational efficiency, and ensures that data is stored on the most cost-effective tier, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing Power Consumption for Sustainable Savings
Summary: Explore various energy-efficient practices and technologies that can significantly reduce power consumption, resulting in long-term cost savings and environmental benefits.
Reducing power consumption is not only beneficial for cost savings but also aligns with organizations’ sustainability efforts. By adopting energy-efficient practices and technologies, businesses can minimize their carbon footprint, lower operational costs, and contribute to a greener future.
One key strategy for reducing power consumption is optimizing server utilization. By implementing server virtualization and consolidating workloads, businesses can reduce the number of physical servers, thereby decreasing power consumption associated with idle or underutilized hardware. Additionally, implementing power management features, such as dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) and server power capping, can further optimize power usage by adjusting server performance based on workload demands.
Efficient Cooling Solutions
Cooling is a significant contributor to data center power consumption. Implementing efficient cooling solutions, such as hot aisle/cold aisle containment, can reduce the energy required for cooling by minimizing the mixing of hot and cold air. Additionally, utilizing energy-efficient cooling technologies, such as economizers or liquid cooling, can provide substantial energy savings by leveraging outside air or liquid-based cooling methods. By optimizing cooling systems, businesses can significantly reduce power consumption and lower their overall operational costs.
Power Monitoring and Management
Implementing power monitoring and management tools allows businesses to track and analyze power usage in real-time. By monitoring power consumption at the server, rack, or data center level, organizations can identify areas of inefficiency and implement targeted measures to reduce power consumption. Power management tools can also provide insights into energy usage patterns, enabling businesses to allocate resources more effectively and identify opportunities for further energy savings. By actively managing power consumption, businesses can achieve sustainable cost savings and contribute to their environmental goals.
Open Source Solutions: Unlocking Cost Savings and Customization
Summary: Learn about the advantages of leveraging open-source software and tools, including cost savings, flexibility, and the ability to customize solutions to specific business needs.
Open-source solutions have gained popularity in the IT industry due to their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and the ability to customize and tailor solutions to specific business requirements. By adopting open-source software and tools for data server strategies, businesses can unlock significant cost savings and enjoy the benefits of a vibrant and collaborative community.
One of the primary advantages of open-source solutions is the elimination of licensing costs. Instead of paying hefty fees for proprietary software, businesses can leverage open-source alternatives, which are often available free of charge. This cost savings can be particularly significant when deploying data servers at scale, as licensing costs can quickly add up. Additionally, the open-source nature of these solutions provides transparency, enabling organizations to assess the security and reliability of the software and make informed decisions.
Flexibility and Customization
Open-source solutions offer unparalleled flexibility and customization options. Businesses can modify the source code to suit their specific needs, add or remove features, and integrate with other systems seamlessly. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor the software to their unique requirements, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Furthermore, the open-source community provides a wealth of resources, documentation, and support, enabling businesses to leverage the expertise of a diverse community and resolve issues more efficiently.
Community Support and Collaboration
The open-source community fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing, providing businesses with access to a vast pool of expertise. By joining the open-source community, organizations can tap into the collective wisdom of developers, users, and contributors, benefiting from their experiences, insights, and best practices. The community-driven development model ensures continuous improvement and innovation, leading to more robust and feature-rich solutions over time. Leveraging open-source solutions not only saves costs but also empowers businesses to actively participate in the development and improvement of the software they rely on.
Proper Capacity Planning: Avoiding Overspending and Underutilization
Summary: Discover the importance of accurate capacity planning and how businesses can avoid overspending on unnecessary resources or encountering performance bottlenecks due to underutilization.
Effective capacity planning is crucial for optimizing data server strategies and ensuring that businesses have the right resources in place to meet current and future demands. By accurately forecasting resource requirements, organizations can avoid overspending on unnecessary infrastructure or encountering performance issues due to underutilization.
One key aspect of capacity planning is analyzing historical data and trends to understand usage patterns and anticipate future needs. By collecting and analyzing data on factors such as server utilization, storage growth, and network traffic, businesses can identify patterns and make informed projections. This data-driven approach enables organizations to allocate resources appropriately, ensuring that they have the necessary capacity to handle workloads without overspending on excessive resources.
Scalability and Elasticity
Scalability and elasticity are critical considerations in capacity planning. Scalability refers to the ability to increase resources, such as adding more servers or storage, to accommodate growing demands. Elasticity, on the other hand, involves the ability to dynamically allocate and deallocate resources based on workload fluctuations. By designing data server strategies with scalability and elasticity in mind, businesses can avoid overprovisioning and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently, maximizing cost savings and performance.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Monitoring server performance is essential for capacity planning. By continuously monitoring key metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O, businesses can identify performance bottlenecks and make informed decisions about resource allocation. This proactive approach enables organizations to optimize server performance, ensure that resources are utilized effectively, and prevent potential performance issues. By closely monitoring and optimizing performance, businesses can achieve cost-effective capacity planning and avoid unnecessary expenditure on additional resources.
Security Measures on a Budget: Prioritizing Protection Without Overspending
Summary: Explore cost-effective cybersecurity measures that organizations can implement to safeguard their data server infrastructure from potential threats without exceeding budget constraints.
Protecting data server infrastructure from security threats is crucial for businesses of all sizes. However, implementing robust security measures can often be expensive. By adopting cost-effective cybersecurity practices, organizations can prioritize protection without compromising their budgetary constraints.
One fundamental aspect of cost-effective cybersecurity is adopting a defense-in-depth approach. This approach involves implementing multiple layers of security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and access controls, to create a layered defense. By combining different security measures, organizations can mitigate risks effectively without relying solely on expensive, single-point solutions.
Routine Patching and Updates
Keeping systems up to date with the latest patches and updates is critical for maintaining security. Many security vulnerabilities are discovered and patched regularly, and organizations must ensure that their data server infrastructure is protected by promptly applying these updates. By establishing a routine patching processand implementing automated patch management tools, businesses can streamline the patching process, reduce the risk of vulnerabilities, and enhance the security of their data servers without incurring additional costs.
Effective Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is essential for protecting data servers from unauthorized access. By enforcing strong passwords, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating user access privileges, organizations can strengthen their security posture without significant financial investments. Additionally, organizations can leverage open-source identity and access management solutions to manage user access effectively, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to critical data and systems.
Employee Training and Awareness
Investing in employee training and awareness programs can be a cost-effective way to enhance cybersecurity. By educating employees about common security threats, best practices for data protection, and the importance of maintaining good cyber hygiene, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of human error and social engineering attacks. Regular training sessions, simulated phishing exercises, and ongoing communication about the latest security trends can empower employees to be more vigilant and proactive in safeguarding data servers.
Implementing Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to prevent lateral movement of threats and contain potential breaches. By strategically segmenting the network and applying access controls between segments, organizations can limit the impact of a security incident and prevent unauthorized access to critical data servers. Network segmentation can be achieved using virtual LANs (VLANs) or software-defined networking (SDN) technologies, which can help organizations achieve cost-effective security without requiring extensive infrastructure investments.
In conclusion, implementing cost-effective data server strategies is not only essential for businesses with limited resources but also beneficial for organizations looking to optimize their expenditure without compromising on performance and security. By embracing cloud computing, virtualization, automation, and energy-efficient practices, while leveraging techniques such as data deduplication, server colocation, and data tiering, businesses can achieve significant cost savings while ensuring efficient data management. Adopting an informed approach and strategically implementing these strategies will undoubtedly pave the way for a cost-effective and robust data server infrastructure, protecting valuable data assets while maximizing efficiency and staying within budgetary constraints.