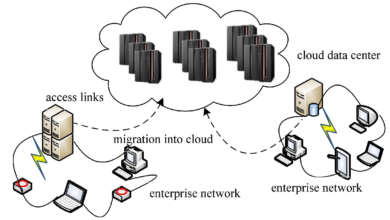
Migrating to Data Servers
Are you considering migrating to data servers for your business? As technology continues to advance, the need for efficient and secure data storage has become more critical than ever. Whether you are moving from an on-premise solution or looking to upgrade your current server infrastructure, this blog article will provide you with all the information you need to ensure a smooth and successful migration process.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the steps involved in migrating to data servers, covering everything from planning and preparation to the actual migration process and post-migration considerations. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of the key factors to consider when making the switch, ensuring minimal downtime and maximum data security.
Assessing Your Current Infrastructure
Before embarking on any migration project, it is crucial to assess your current infrastructure and determine your specific needs and requirements. This section will guide you through the process of evaluating your current server setup and identifying any potential bottlenecks or limitations.
Evaluating Performance and Scalability
One of the first steps in assessing your current infrastructure is evaluating the performance and scalability of your existing servers. Consider factors such as processing power, memory, storage capacity, and network bandwidth. Identify any areas where your current servers may be struggling to meet the demands of your business.
Identifying Potential Bottlenecks
Next, you’ll need to identify any potential bottlenecks in your current infrastructure. This includes analyzing your network architecture, server configurations, and storage systems. Look for any areas where data transfer speeds are slow or where there may be limited redundancy and fault tolerance.
Assessing Security Measures
Security is paramount when it comes to data storage. Evaluate the current security measures in place, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls. Identify any vulnerabilities or areas where security can be improved to ensure the safety and integrity of your data.
Considering Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Depending on your industry, you may have specific compliance and regulatory requirements that need to be considered during the migration process. Evaluate whether your current infrastructure meets these requirements and determine if migrating to data servers can help you achieve better compliance and data governance.
Choosing the Right Data Server Solution
With a wide range of data server options available in the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right solution for your business. In this section, we will discuss the various types of data servers, their pros and cons, and guide you in selecting the most suitable option for your specific needs.
Understanding On-Premise Data Servers
On-premise data servers are physical servers that are located within your organization’s premises. They offer complete control over your data and infrastructure but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of on-premise servers to determine if they are the right fit for your business.
Exploring Cloud-based Data Servers
Cloud-based data servers, on the other hand, provide a flexible and scalable solution that eliminates the need for on-site hardware. Consider the advantages of cloud-based servers, such as reduced upfront costs, increased scalability, and simplified maintenance. Assess whether a cloud-based solution aligns with your business goals and requirements.
Weighing Hybrid Data Server Solutions
Hybrid data server solutions combine the benefits of on-premise and cloud-based servers. They offer the flexibility to store sensitive or critical data on-premise while leveraging the scalability and cost-efficiency of the cloud for less critical applications. Evaluate whether a hybrid solution can provide the best of both worlds for your organization.
Considering Managed Data Server Services
If managing and maintaining data servers is not within your organization’s core expertise, you may want to consider managed data server services. These services provide expert support and management for your data servers, allowing you to focus on your core business activities. Assess the benefits and costs associated with managed services to determine if they are a viable option for your organization.
Planning and Preparation
Proper planning and preparation are essential to ensure a successful migration. This section will walk you through the key steps involved in planning and preparing for the migration process, including data backup, resource allocation, and establishing a timeline.
Creating a Migration Plan
Start by creating a detailed migration plan that outlines the specific tasks, timelines, and responsibilities for each stage of the migration process. This plan will serve as a roadmap to ensure that all necessary steps are taken and nothing is overlooked during the migration.
Backing Up Your Data
Prior to the migration, it is crucial to back up all your data to prevent any potential loss or corruption during the transition. Evaluate your current backup strategy and ensure that all critical data is securely backed up. Consider using multiple backup methods, such as cloud-based backups and physical backups, for added redundancy.
Allocating Sufficient Resources
Migrating to data servers may require additional hardware, software, or network resources. Assess your current resource allocation and determine if any upgrades or expansions are necessary to support the new data server environment. Consider factors such as storage capacity, network bandwidth, and processing power to ensure optimal performance.
Establishing a Migration Timeline
Set a realistic migration timeline that takes into account the complexity of your infrastructure, the amount of data to be migrated, and any potential downtime or disruption to your business operations. Communicate the timeline to all stakeholders and ensure that everyone is aware of their roles and responsibilities during the migration process.
Communicating with Stakeholders
Effective communication is key to a successful migration. Inform all relevant stakeholders, including employees, clients, and vendors, about the upcoming migration and any potential impact on their operations. Address any concerns or questions they may have and provide regular updates throughout the migration process to keep everyone informed.
Data Migration Strategies
There are multiple data migration strategies available, each with its own advantages and considerations. In this section, we will explore different migration strategies, such as physical migration, virtual migration, and hybrid migration, and help you choose the most suitable approach for your business.
Physical Migration
Physical migration involves physically moving data from one server or storage system to another. This strategy is often used when migrating from on-premise servers to cloud-based servers or when transferring large amounts of data. Evaluate the benefits and challenges of physical migration, such as the logistics of transporting physical hardware and the potential for downtime during the transition.
Virtual Migration
Virtual migration involves copying data from one server to another using virtualization technologies. This strategy is useful when migrating between similar server architectures or when the physical distance between servers is not a factor. Consider the advantages of virtual migration, such as reduced downtime and the ability to test the migration process in a controlled environment.
Hybrid Migration
Hybrid migration combines elements of both physical and virtual migration strategies. This approach is often used when migrating complex or heterogeneous server environments. Evaluate whether a hybrid migration can provide the flexibility and efficiency needed for your specific migration requirements.
Testing and Validation
Before finalizing the migration process, thorough testing and validation are crucial to ensure data integrity and minimize any potential issues. This section will guide you through the testing and validation phase, providing best practices and tips to ensure a smooth transition.
Creating a Test Environment
Set up a separate test environment that closely mirrors your production environment. This will allow you to simulate the migration process and identify any potential issues or conflicts before migrating your live data. Ensure that the test environment is isolated and does not impact your production systems.
Performing Data Integrity Checks
Ensure the integrity of your data by performing thorough data integrity checks before and after the migration. Use checksums or hashing algorithms to verify the accuracy and completeness of the data during the migration process. This will help identify any data corruption or loss that may have occurred during the migration.
Testing Application Compatibility
Test the compatibility of your applications with the new data server environment. Some applications may require configuration changes or updates to work seamlessly with the new infrastructure. Identify any compatibility issues and address them before migrating your live data to avoid any disruptions to your business operations.
Validating Performance and Functionality
Once the data migration is complete, thoroughly test the performance and functionality of your applications and systems in the new data server environment. Monitor key performance metrics, such as response times and throughput, to ensure that the new infrastructure meets your performance expectations. Address any performance issues or bottlenecks that may arise during the validation phase.
Creating a Rollback Plan
Despite careful planning and testing, there is always a possibility of unforeseen issues during the migration process. Create a rollback plan that outlines the steps to revert back to the previous server environment in case of any major issues or failures. This will provide you with a safety net and minimize the impact of any potential setbacks.
Execution and Monitoring
Once the planning and testing phases are complete, it’s time to execute the migration. This section will provide a detailed walkthrough of the migration process, including data transfer, server setup, andmonitoring during the transition to ensure a seamless migration.
Data Transfer and Migration
Begin the migration process by transferring your data from the source server to the destination server. Depending on the chosen migration strategy, this may involve physical relocation of hardware, virtual copying of data, or a combination of both. Follow the migration plan and ensure that all data is transferred accurately and securely.
Server Setup and Configuration
Once the data is successfully migrated, set up and configure the new data server environment according to your specific requirements. This may include installing operating systems, configuring network settings, and optimizing storage allocation. Follow best practices and ensure that the new server environment is properly secured and optimized for performance.
Testing the New Server Environment
After the server setup is complete, thoroughly test the new server environment to ensure that it is functioning as expected. Verify that all applications and services are running smoothly and perform additional performance and functionality tests. Monitor the system closely for any anomalies or issues that may require further adjustments or optimization.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Throughout the migration and post-migration process, it is crucial to monitor the new data server environment for any performance issues, security vulnerabilities, or other potential problems. Implement monitoring tools and establish regular checks to identify and address any issues promptly. Continuously monitor system performance, network traffic, disk utilization, and security logs to ensure the stability and security of your data server environment.
User Acceptance Testing
Engage key stakeholders and end-users in user acceptance testing to ensure that the new data server environment meets their needs and expectations. Gather feedback and address any usability or functional concerns that may arise. User acceptance testing provides valuable insights and helps fine-tune the new environment to optimize user experience and productivity.
Ngadsen test2
Post-Migration Considerations
After the migration is complete, there are several post-migration considerations to take into account. This section will guide you through the necessary steps to ensure data consistency, security, and performance optimization in your new data server environment.
Data Consistency and Validation
Verify the consistency and integrity of your data in the new data server environment. Compare the migrated data with the original source to ensure that all data has been accurately transferred. Perform data validation checks and resolve any discrepancies or issues that may arise during the validation process.
Updating System Documentation
Update your system documentation to reflect the changes made during the migration process. This includes updating server configurations, network diagrams, and any other relevant documentation. Keeping accurate and up-to-date documentation will facilitate future troubleshooting, maintenance, and future migrations.
Optimizing Performance and Resource Allocation
Continuously monitor and optimize the performance of your new data server environment. Analyze system performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk I/O, to identify any bottlenecks or areas for improvement. Adjust resource allocation as needed to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
Implementing Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions
Data backup and disaster recovery should be a top priority in your new data server environment. Implement a robust backup strategy that includes regular backups, offsite storage, and periodic testing of restore processes. Consider implementing disaster recovery solutions, such as redundant server configurations or failover systems, to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity in the event of a system failure.
Enhancing Data Security Measures
Review and enhance your data security measures in the new data server environment. This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Regularly patch and update your server software to address any security vulnerabilities. Stay informed about emerging threats and best practices in data security to proactively protect your data against potential risks.
Training and Educating Users
Ensure that your users are trained and educated on the new data server environment. Conduct training sessions to familiarize users with any changes in workflows, access controls, or system interfaces. Provide ongoing support and resources to help users adapt to the new environment and maximize their productivity.
Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining the health and performance of your data server environment is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor system logs, performance metrics, and security alerts to identify and address any issues promptly. Regularly perform system maintenance tasks, such as software updates, hardware checks, and disk defragmentation, to keep your data servers running smoothly.
Data Server Maintenance and Optimization
Regular maintenance and optimization are vital to keep your data servers running smoothly and efficiently. In this section, we will discuss best practices for server maintenance, performance monitoring, and optimization techniques.
Performing Regular System Updates
Keep your data servers up to date by regularly installing software updates, patches, and security fixes. These updates often include important bug fixes, performance enhancements, and security patches that help protect your data and ensure optimal system performance. Establish a regular schedule for applying updates and ensure that they are thoroughly tested before deployment.
Monitoring Performance Metrics
Continuously monitor performance metrics to identify any bottlenecks or areas for improvement. Track metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, and network bandwidth to pinpoint potential performance issues. Use monitoring tools to set up alerts and notifications for critical performance thresholds to ensure prompt action when needed.
Optimizing Storage Allocation
Regularly review and optimize your storage allocation to ensure efficient use of resources. Identify any underutilized or overutilized storage volumes and make necessary adjustments. Implement storage optimization techniques such as data compression, deduplication, or tiered storage to maximize storage capacity and optimize performance.
Implementing Load Balancing
If you have multiple data servers, consider implementing load balancing techniques to distribute the workload evenly across servers. Load balancing helps optimize system performance by preventing any single server from becoming overloaded. Evaluate different load balancing algorithms and implement the one that best suits your workload and infrastructure.
Monitoring Network Traffic
Monitor network traffic to identify any abnormal patterns or potential security threats. Implement network traffic monitoring tools to detect and analyze network traffic in real-time. Regularly review network logs and implement intrusion detection systems to identify and mitigate any unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activity.
Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Testing
Regularly test your backup and disaster recovery processes to ensure that your data can be restored successfully in the event of a system failure or data loss. Perform periodic backups and simulate different disaster scenarios to validate the effectiveness of your backup and recovery procedures. Make any necessary adjustments or improvements based on the results of these tests.
Data Security and Backup
Data security should be a top priority when migrating to data servers. This section will delve into the importance of data security, best practices for securing your data servers, and implementing a robust backup strategy to protect against data loss.
Implementing Access Controls
Control access to your data servers by implementing strong authentication measures and access controls. Use strong passwords or multi-factor authentication to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the servers. Implement role-based access controls to limit privileges based on job responsibilities and the principle of least privilege.
Encrypting Data in Transit and at Rest
Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access. Use secure communication protocols such as SSL/TLS when transferring data over networks. Encrypt data stored on your data servers using encryption algorithms and ensure that encryption keys are properly managed and protected.
Regularly Monitoring and Auditing Access
Monitor and audit access to your data servers to detect and respond to any unauthorized or suspicious activity. Implement logging and auditing mechanisms to track user activities, file access, and system changes. Regularly review access logs and audit trails to identify any anomalies or potential security breaches.
Implementing Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Protect your data servers from external threats by implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems. These systems monitor network traffic and server logs for any signs of unauthorized access or suspicious activity. Configure alerts and notifications to receive real-time notifications of any potential security incidents.
Regularly Updating and Patching Software
Keep your server software up to date by regularly applying updates and security patches. Software updates often include critical security fixes that address known vulnerabilities. Establish a regular schedule for applying updates and patches and ensure that they are thoroughly tested before deployment.
Implementing a Robust Backup Strategy
Implement a comprehensive backup strategy to protect your data against loss or corruption. Regularly back up your data servers to an offsite location or cloud-based storage. Consider implementing incremental or differential backups to reduce backup times and storage requirements. Test your backup and recovery processes regularly to ensure that data can be restored successfully in case of a disaster.
Testing Data Recovery Procedures
Regularly test your data recovery procedures to ensure that your backups are valid and can be restored successfully. Perform test restores of your backed-up data to verify their integrity and completeness. This will help identify any issues or gaps in your backup strategy and allow you to make necessary adjustments or improvements.
Future Scalability and Growth
As your business evolves, scalability becomes a crucial factor. This section will discuss the importance of planning for future growth and scalability when migrating to data servers, ensuring your infrastructurecan adapt to your changing business needs.
Assessing Future Storage Requirements
Anticipate your future storage needs by assessing your data growth rate and projected data volumes. Consider factors such as new applications, increased user base, and emerging technologies that may contribute to data growth. Evaluate your current storage capacity and plan for future expansion to accommodate the growing data requirements.
Scalable Server Architecture
Choose a data server solution that offers scalability in terms of both storage capacity and processing power. Opt for server architectures that allow for seamless addition of storage devices or the ability to upgrade hardware components without disrupting operations. A scalable server architecture ensures that your infrastructure can grow with your business.
Flexible Network Infrastructure
Ensure that your network infrastructure is flexible enough to accommodate future growth and increased data traffic. Implement network switches, routers, and cabling that can handle higher bandwidth requirements. Consider technologies like virtual LANs (VLANs) or software-defined networking (SDN) that provide flexibility and scalability in network management.
Cloud Integration and Hybrid Solutions
Consider integrating cloud services into your data server infrastructure to enhance scalability. Cloud solutions provide virtually unlimited storage capacity and computing power, allowing you to scale resources as needed. Explore hybrid cloud solutions that combine on-premise servers with cloud-based storage and processing for a flexible and scalable infrastructure.
Future-proofing Data Architecture
Design your data architecture with future scalability in mind. Consider implementing data partitioning or sharding techniques to distribute data across multiple servers. Adopt data storage technologies that support horizontal scaling, such as distributed file systems or NoSQL databases. Future-proofing your data architecture ensures that your infrastructure can handle increased data volumes and user demands.
Regular Capacity Planning
Perform regular capacity planning exercises to assess your infrastructure’s ability to handle future growth. Evaluate system performance, storage utilization, and network traffic to identify potential bottlenecks or areas that may require additional resources. Use capacity planning tools and techniques to forecast future resource requirements and make informed decisions about infrastructure upgrades or expansions.
Flexible Licensing and Vendor Agreements
When selecting data server solutions, consider the flexibility of licensing models and vendor agreements. Choose vendors that offer scalable licensing options, allowing you to easily add or remove licenses as your needs change. Negotiate flexible vendor agreements that accommodate future growth and provide room for expansion without incurring significant costs or penalties.
Continuous Evaluation and Optimization
Regularly evaluate and optimize your data server infrastructure to ensure that it remains aligned with your business goals and future scalability needs. Periodically review your infrastructure’s performance, security, and capacity to identify areas for improvement. Implement optimization strategies, such as data compression, deduplication, or load balancing, to maximize resource utilization and enhance scalability.
Migrating to data servers is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and maintenance. By following the steps and considerations outlined in this comprehensive guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to ensure a seamless and successful migration. Remember, thorough assessment, proper planning, and ongoing optimization are key to maximizing the benefits of your new data server environment. Embrace the opportunities that data servers bring and propel your business into the digital age with confidence.