Scaling E-commerce with Data Servers
In today’s digital age, e-commerce has revolutionized the way businesses operate. With the ever-increasing number of online shoppers, it has become crucial for e-commerce businesses to scale their operations effectively. One efficient way to achieve this is by leveraging data servers. In this blog article, we will explore the various aspects of scaling e-commerce with data servers, providing you with a unique, detailed, and comprehensive guide.
Firstly, we will delve into the importance of data servers for e-commerce scaling. We will discuss how data servers can handle the increasing volume of online transactions, ensuring seamless customer experiences. Additionally, we will explore the role of data servers in managing and analyzing vast amounts of customer data, enabling personalized marketing and improved decision-making.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Data Servers
Data servers are the backbone of e-commerce operations, handling the storage and processing of critical data. To understand their significance in scaling e-commerce, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of these servers. Data servers are specialized computers designed to store, manage, and retrieve data. They consist of hardware components, including processors, memory, and storage devices, along with software that enables efficient data management.
Architecture of Data Servers
Data servers usually follow a client-server architecture, where the server hosts and manages the data, while clients access and interact with the data through various applications or websites. This architecture allows businesses to provide uninterrupted services to their customers, even during high traffic periods. Additionally, data servers can be deployed in different configurations, such as standalone servers or clusters, depending on the scalability requirements of the e-commerce business.
Types of Data Servers
There are various types of data servers available for e-commerce businesses, each with its own advantages and use cases. Traditional servers, also known as bare-metal servers, are physical servers dedicated to a single business or organization. They provide high performance and complete control over the hardware. On the other hand, cloud servers offer scalability and flexibility by leveraging virtualization technologies. Cloud servers are hosted in data centers and can be easily scaled up or down based on the business needs.
Virtual private servers (VPS) are a popular choice for small to medium-sized e-commerce businesses as they provide a balance between cost and performance. VPSs are virtualized servers that share the physical resources of a host server but operate independently. Finally, there are managed hosting solutions, where the hosting provider takes care of server management and maintenance, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
Optimizing Server Performance for E-commerce
Server performance plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth e-commerce operations. When scaling an e-commerce business, it’s essential to optimize server performance to handle increasing website traffic, reduce latency, and provide a seamless user experience. There are several strategies and techniques that businesses can employ to optimize their server performance.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is a technique that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure efficient utilization of resources. By evenly distributing the load, businesses can prevent any single server from becoming overloaded, thus enhancing performance and providing scalability. Load balancing can be achieved through various methods, including round-robin, weighted round-robin, least connection, or even using intelligent algorithms that consider server health and capacity.
Caching
Caching involves storing frequently accessed data or web pages in a cache, closer to the user, to reduce the need for repeated retrieval from the server. This technique improves response times and reduces the load on the server. Caching can be implemented at different levels, such as browser caching, reverse proxy caching, or content delivery network (CDN) caching. By leveraging caching mechanisms, e-commerce businesses can provide faster and more responsive experiences to their customers.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs are a network of servers distributed geographically, strategically placed closer to end-users to deliver content efficiently. CDNs store cached versions of static website content, such as images, videos, and JavaScript files, in multiple locations worldwide. When a user requests content, the CDN routes the request to the nearest server, reducing latency and improving website performance. Implementing a CDN can significantly enhance the loading speed of e-commerce websites, leading to better user experiences and increased customer satisfaction.
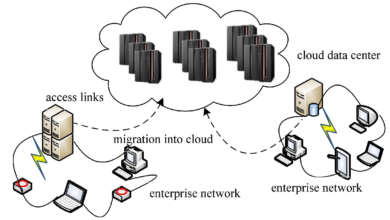
Scaling E-commerce with Cloud Servers
Cloud servers have revolutionized the way e-commerce businesses scale their operations. Cloud infrastructure offers unparalleled scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, making it an ideal choice for businesses looking to expand rapidly. Scaling e-commerce with cloud servers involves utilizing the resources and services provided by cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Scalability of Cloud Servers
One of the key advantages of cloud servers is their ability to scale dynamically based on the demand. With traditional servers, businesses would need to invest in additional hardware and infrastructure to accommodate increased traffic. However, cloud servers allow businesses to scale up or down instantly, paying only for the resources they consume. This scalability ensures that e-commerce websites can handle sudden spikes in traffic during seasonal sales or marketing campaigns without any performance degradation.
Cost-effectiveness of Cloud Servers
Cloud servers offer cost-effectiveness by eliminating the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Businesses can avoid the expenses associated with purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading physical servers. With cloud servers, businesses only pay for the resources they utilize, allowing them to optimize costs based on their actual requirements. Additionally, cloud service providers offer various pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go or reserved instances, enabling businesses to choose the most cost-effective option for their e-commerce scaling needs.
Flexibility of Cloud Servers
Cloud servers provide unparalleled flexibility for e-commerce businesses. They offer a wide range of services and resources that can be easily provisioned and configured to meet specific requirements. Whether it’s computing power, storage capacity, or specialized services like databases or AI frameworks, cloud service providers offer a vast array of options. This flexibility allows businesses to scale their e-commerce operations seamlessly, experiment with new features or technologies, and quickly adapt to changing market dynamics.
Challenges and Solutions with Cloud Servers
While cloud servers offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges that businesses need to address. One of the primary concerns is ensuring data security and compliance. As data is stored on remote servers managed by cloud service providers, businesses must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, businesses need to consider factors like data sovereignty, vendor lock-in, and the potential impact of service outages. By carefully assessing these challenges and implementing appropriate solutions, businesses can leverage cloud servers effectively for e-commerce scaling.
Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Data security is of utmost importance for e-commerce businesses as they handle sensitive customer information, including personal details and payment credentials. When scaling e-commerce with data servers, businesses must ensure that their data security measures are robust and comply with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Encryption Techniques
Encryption is a fundamental technique to protect data from unauthorized access. E-commerce businesses should implement strong encryption algorithms to encrypt data both at rest and in transit. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols can be employed to secure communications between servers and clients, ensuring that data remains confidential and cannot be intercepted by malicious actors.
Access Controls
Implementing access controls ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive e-commerce data. Role-based access control (RBAC) can be employed to assign specific roles and permissions to users, restricting their access to data based on their responsibilities. Additionally, businesses should regularly review and update access controls to ensure that access privileges are granted on a need-to-know basis, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Compliance with Regulations
E-commerce businesses must comply with various regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for handling payment card information. Compliance involves implementing appropriate measures to protect customer data, providing transparency regarding data collection and processing practices, and establishing procedures for data breach notifications. By adhering to these regulations, businesses can ensure the privacy and trust of their customers, maintaining their reputation in the market.
Leveraging Big Data Analytics for E-commerce Scaling
Big data analytics plays a pivotal role in driving growth for e-commerce businesses. By leveraging data servers, businesses can analyze vast amounts of customer data and gain valuable insights that drive decision-making, optimize marketing strategies, and improve operational efficiency.
Understanding Customer Behavior
One of the primary benefits of big data analytics for e-commerce is understanding customer behavior. By analyzing customer data, such as browsing patterns, purchase history, and demographic information, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences, interests, and buying patterns. These insights enable businesses to personalize marketing efforts, recommend relevant products, and provide tailored experiences, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Optimizing Marketing Strategies
Data analytics allows businesses to optimize their marketing strategies by identifying trends and patterns in customer behavior. By analyzing data related to marketing campaigns, businesses can determine the effectiveness of different channels, messaging, and promotional offers. This insight enables businesses to allocate resources effectively, optimize their marketing spend, and improve their return on investment (ROI).
Ngadsen test2
Improving OperationalEfficiency
Big data analytics also helps businesses improve their operational efficiency. By analyzing data on inventory levels, supply chain processes, and customer demand, businesses can optimize their inventory management, reduce stockouts, and streamline their operations. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, minimize costs, and ensure timely order fulfillment, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is another powerful application of big data in e-commerce scaling. By leveraging historical data and advanced algorithms, businesses can forecast future trends, customer behavior, and demand patterns. This enables businesses to proactively plan their inventory, marketing campaigns, and resource allocation, ensuring they can meet customer needs and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Implementing Real-time Data Processing
Real-time data processing is essential for e-commerce businesses to provide personalized experiences and make data-driven decisions. Data servers play a crucial role in enabling real-time data processing, ensuring that businesses can extract insights, respond quickly to customer actions, and deliver dynamic content.
Apache Kafka for Real-time Data Streaming
Apache Kafka is a popular open-source platform that enables real-time data streaming and processing. It allows businesses to collect, process, and analyze data in real-time, making it ideal for e-commerce scaling. With Kafka, businesses can capture and process vast amounts of data streams from various sources, including website interactions, clickstream data, and social media feeds. This enables businesses to gain real-time insights into customer behavior, detect anomalies, and trigger immediate actions or personalized recommendations.
Apache Storm for Real-time Analytics
Apache Storm is another open-source system that is widely used for real-time data processing and analytics. It provides a distributed, fault-tolerant framework for processing large volumes of data streams in real-time. E-commerce businesses can leverage Apache Storm to perform complex analytics tasks, such as real-time fraud detection, sentiment analysis, or recommendation engine updates. By processing data in real-time, businesses can deliver personalized experiences, optimize marketing campaigns on the fly, and respond quickly to changing market dynamics.
Scaling International E-commerce Operations
Expanding e-commerce operations globally presents unique challenges. However, data servers play a vital role in facilitating the scaling of international e-commerce operations, enabling businesses to overcome geographical barriers and provide localized experiences to their international customers.
Geo-targeting for Personalized Experiences
Geo-targeting is a technique that allows businesses to deliver personalized content and experiences based on the user’s geographical location. By leveraging data servers, businesses can identify the location of their customers and serve them localized content, such as language preferences, currency conversion, or region-specific promotions. This enhances the customer experience, increases engagement, and fosters a sense of familiarity and relevance.
Content Delivery Strategies
When scaling international e-commerce operations, businesses need to ensure that content is delivered efficiently to customers in different regions. Content delivery strategies include leveraging CDNs, hosting regional servers, or using edge computing technologies. CDNs help reduce latency by caching content closer to end-users, ensuring fast and reliable access to e-commerce websites. Hosting regional servers allows businesses to store data in close proximity to customers, minimizing data transfer delays. Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the network edge, enabling faster processing of localized data and reducing reliance on centralized servers.
Multi-Region Data Centers
Setting up multi-region data centers is another strategy for scaling international e-commerce operations. By establishing data centers in different geographical locations, businesses can distribute their infrastructure and data storage across regions, ensuring resilience, scalability, and compliance with local data regulations. Multi-region data centers allow businesses to optimize data transfer speeds, reduce latency, and provide a consistent user experience to customers across different locations.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in E-commerce Scaling
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed the e-commerce landscape, enabling businesses to automate processes, enhance customer interactions, and drive revenue growth. Data servers play a crucial role in supporting AI applications in e-commerce scaling.
AI-Powered Chatbots
Chatbots are virtual assistants that use AI algorithms to simulate human-like conversations with customers. By leveraging data servers for natural language processing and machine learning, businesses can deploy AI-powered chatbots to handle customer inquiries, provide product recommendations, and assist with order tracking. AI-powered chatbots not only enhance customer service but also reduce customer support costs and improve response times.
Recommendation Engines
Recommendation engines are AI algorithms that analyze customer data to provide personalized product recommendations. By utilizing data servers for processing and analyzing vast amounts of customer data, businesses can build sophisticated recommendation engines that suggest relevant products based on user behavior, purchase history, and preferences. This improves cross-selling and upselling opportunities, increases customer engagement, and drives revenue growth.
Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Predictive analytics, powered by AI and data servers, can significantly impact demand forecasting for e-commerce businesses. By analyzing historical sales data, customer behavior, and external factors, businesses can predict future demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and ensure timely restocking. This minimizes stockouts, reduces inventory carrying costs, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
Scalable Database Solutions for E-commerce
A robust and scalable database is essential for managing the increasing volume of e-commerce data. Data servers enable businesses to implement scalable database solutions that can handle the growing demands of e-commerce operations.
Relational Databases
Relational databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle, have been the traditional choice for e-commerce businesses. They provide a structured and organized way to store and retrieve data, ensuring consistency and integrity. By leveraging data servers for relational databases, businesses can scale their operations by optimizing database performance, implementing efficient indexing strategies, and ensuring high availability through replication and clustering techniques.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, Cassandra, or Redis, are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. They offer horizontal scalability, allowing businesses to distribute data across multiple servers or clusters. Data servers play a crucial role in supporting NoSQL databases by providing the necessary computing power, storage capacity, and network connectivity to handle the increased workload. By leveraging NoSQL databases and data servers, businesses can scale their e-commerce operations efficiently and handle diverse data types.
Distributed Database Systems
Distributed database systems, such as Apache Hadoop or Google BigQuery, offer scalable and fault-tolerant solutions for managing large datasets. These systems distribute data across multiple servers or clusters, enabling parallel processing and high availability. Data servers play a critical role in supporting distributed database systems by providing the necessary computational resources and storage capacity. By leveraging distributed database systems, businesses can handle massive amounts of e-commerce data, perform complex analytics, and extract valuable insights for scaling their operations.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Continuous monitoring and performance optimization are crucial for maintaining the scalability of an e-commerce infrastructure. By regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and implementing proactive measures, businesses can ensure that their data servers and overall infrastructure operate optimally.
Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring involves tracking and analyzing various metrics to assess the health and efficiency of data servers. Businesses can monitor metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, network throughput, and response times. By leveraging monitoring tools and techniques, businesses can identify performance bottlenecks, detect anomalies, and take proactive measures to optimize server performance. Monitoring can be done through a combination of server-level monitoring, application-level monitoring, and network monitoring.
Load Testing
Load testing involves simulating high traffic scenarios to assess the performance and scalability of data servers. By subjecting the servers to realistic loads, businesses can identify any performance limitations and ensure that the infrastructure can handle peak traffic without degradation. Load testing can be performed using specialized tools and techniques that simulate concurrent users, simulate different types of requests, and measure response times. By conducting regular load tests, businesses can proactively identify and address any performance issues before they impact the user experience.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves forecasting resource requirements based on historical data, growth projections, and expected workload patterns. By analyzing trends and patterns, businesses can estimate future resource needs, such as CPU, memory, and storage capacity. This enables businesses to scale their data servers and infrastructure proactively, ensuring that they can handle increasing demands without performance degradation or resource constraints. Capacity planning also helps businesses optimize costs by ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
In conclusion, scaling e-commerce with data servers is imperative for businesses to thrive in the competitive online marketplace. By understanding the fundamentals of data servers, optimizing server performance, leveraging cloud servers, ensuring data security, harnessing big data analytics and AI, implementing scalable database solutions, and monitoring and optimizing performance, businesses can achieve seamless scalability and provide exceptional customer experiences. With the comprehensive guide provided in this article, you are now equipped with the knowledge to effectively scale your e-commerce operations using data servers.